Cooling systems have evolved over the years, and in this article, this artical will discuss data center cooling options, methods, and the best practices for your data center. We will also discuss new innovations that may be ahead in the coming years. (Published by Michael Isberto)
What Are Some Data Center Cooling Methods?
Traditionally, there are two ways of cooling a data center: air-based cooling and liquid-based cooling.
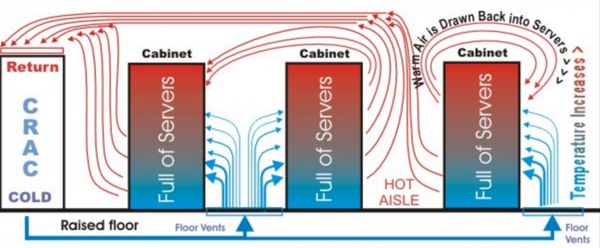
Photo Source: Submer
Air-Based
The first and most common, method within the realm of air-based cooling is what’s called ‘cold aisle/hot aisle.’ The idea is to separate the cold air from the hot air. This is done by facing the cold sides of each cabinet away from the hot sides of each cabinet, which creates a sort of convection system where the cabinets cool themselves. But this does not always work, and the data center managers have to pump a larger amount of cold air in. This older, inefficient method has limitations, which is why many data centers are moving towards new innovations.
A similar process is called ‘cold or hot air containment’ focused on improving the older cold aisle/hot aisle method by physically isolating and containing the servers so the hot and cold air does not mix. Driving the air directly from the CRAC unit helps achieve this. This method works fairly well, but it does have the issue of hot spots.
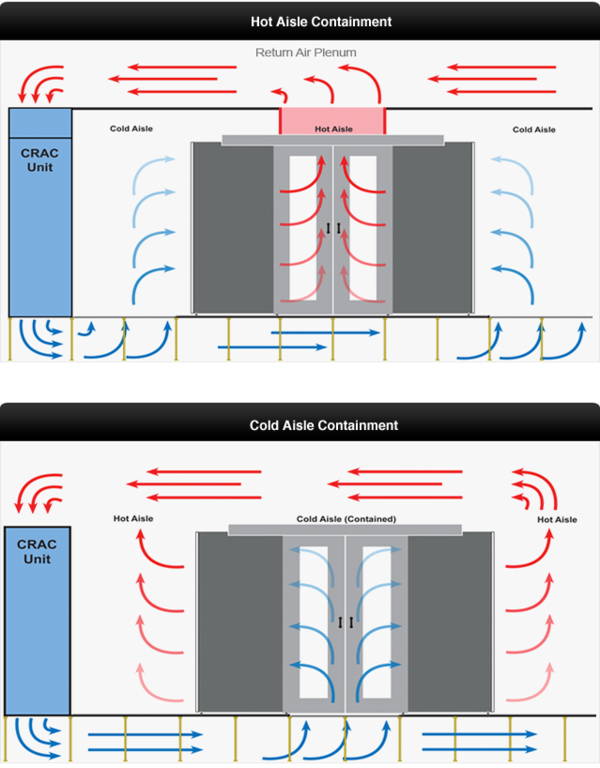
Photo Source: Submer
The last method in the territory of air-based cooling is in-rack heat extraction. This method tries to achieve the same end goal of removing hot air but is done so by having compressors and chillers built into the rack itself. According to Schneider Electric, both Hot Aisle Containment (HACS) and Cold Aisle Containment (CACS) can provide savings. Hot aisle containment can provide 40% more savings than the Cold Aisle Containment. CACS traps the cold air within the system letting the rest of the data center become a hot-air return. While the HACS traps hot air and lets it leave through an exhaust system.
Liquid-Based
Water-cooled racks and servers are the first methods in liquid-based cooling. In this method, water is used to cool the hot side of the cabinet to bring the temperature down. Because water conducts electricity, the water never touches the actual components. The water is contained in basins, which then flows through pipes through cooling tower pumps. The water then runs alongside the server behind a barrier. The cold water helps bring down the temperature of the components inside. This method works well, but the risk of leaks scares many data center managers from using it.
liquid immersion cooling
The next liquid-based cooling method is liquid immersion cooling. In this method, liquid coolant flows across the hot components of a server cooling it down. The servers are fully emerged into the fluid. The way this is done is by using a dielectric fluid. This type of fluid does not conduct electricity but can damage components if not used properly. If this sparks your interest—read more here.
What is An Evaporative Cooled Data Center?
Evaporative cooling is an old technology that is being incorporated to cool machines in data centers. Evaporative cooling is also known as swamp cooling. This type of cooling system is fairly simple.
Evaporative cooling takes the process of water evaporation and applies it to cool data centers. These swamp coolers have a wet pad or a wet filter. Excess heat is dissipated in the water of these pads or filters, which then cools the data center. This type of cooling works best in low humidity climates, like Los Angeles. The only power that evaporative cooling needs are for the fan and the water pump. It doesn’t need a compressor that most other cooling systems use. Evaporative cooling or swamp cooling is so simple and needs so little power that it also has the nickname “free cooling” as well.
evaporative cooling data center
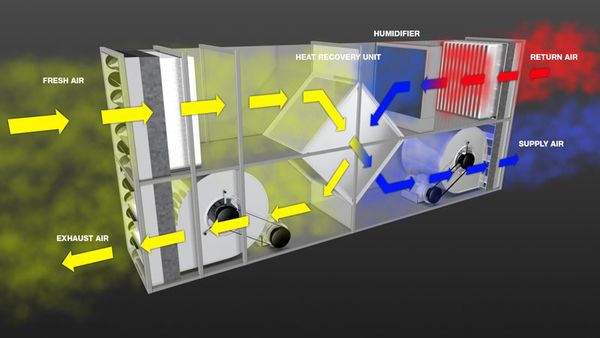
Photo Source: Condair
Although the cost of evaporative cooling is more affordable than the most data center cooling systems, it is far from free. The average cost of evaporative cooling is 25% of traditional HVAC systems. Also, evaporative or swamp cooling comes at other costs. The term swamp cooling is not by accident. This type of system brings higher humidity levels into the data center, which typically isn’t good for any computer equipment. This is why evaporative cooling works best in dry climates or low humidity environments so the humidity levels even out.
Evaporative cooling is a great way for data centers to decrease their overall power usage significantly.
How CryptoCurrency Changed the Data Center Cooling Industry
Green Revolution Cooling, who patented the liquid immersion cooling technology, has seen a tremendous increase in sales this past year. A lot of this can be contributed to the mining of cryptocurrencies including bitcoin.
It takes a lot of power to mine cryptocurrency, which means the servers within the data center have to work harder as well. Because of this, Green Revolution Cooling was able to sell more cooling systems.
Crypto mining GRC HashRaQ data center cooling

Photo Source: Green Revolution Cooling
The demand for liquid immersion cooling was so high because of the crypto craze that GRC produced and recently launched new products, particularly for crypto mining. GRC’s HashRaQ is designed as a single-rack immersion system, and HashTank is designed for a six-rack system. With these two new products, Green Revolution Cooling increased their revenue five times what it had been three years prior.
Although we don’t quite know the lasting nature of cryptocurrency in our society—we do know that cryptocurrency has changed the way we look at data center cooling. We have seen specific data center cooling innovations because of cryptocurrency mining.
What Are Some New Data Center Cooling Systems and Innovations?
There are many innovations from different companies that are changing the landscape of data center cooling. One notable mention is Google’s environmentally friendly data center. The search engine company is using seawater to cool one of their data centers in Hamina, Finland. This system doesn’t need to burn any carbon but instead uses the cold water to cool the mechanism. In this system, Facebook also uses captured rainwater to do the same.
Data center smart assistant and AI technology is also an important innovation when it comes to cooling a data center. It is reported that data centers use 75 percent more cooling than needed. According to datacenterknowledge.com (linked above), cooling a data center is there for risk management, but the amount of money spent on cooling is more than required. A smart assistant like AdeptDC helps data centers save on costs because it lets you know the data center manager know when and how much cooling is needed. It uses smart cooling and machine learning to read CPU and GPU temperatures and processes that data in real time. This software will help data centers become more cooling efficient.
robot monitors data cooling

Photo Source: data center knowledge
Another new innovation is a data center cooling robot that monitors the temperature and humidity levels of the server from the inside of the cabinet. The OneNeck robot sensor is placed on the bottom of the cabinet and moves to the top and back down again scanning for heat and humidity levels. The robot is able to detect hot spots within the rack. One can check these levels from their smart device never having to open up the cabinet. This technology is smarter and more efficient allowing managers to cool only areas that need cooling. Instead of wasting energy cooling the entire data center.
StatePoint Liquid Cooling Facebook Nortek
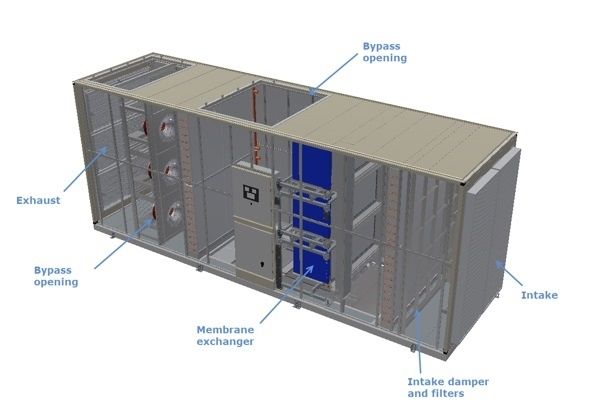
Photo Source: Data Center Dynamics
Facebook and Nortek Air Solutions have also collaborated on an indirect cooling system called StatePoint Liquid Cooling (SPLC). One of the main differences between SPLC and evaporative cooling is the SPLC uses cold water to cool the air instead of using cold air to cool the water. Through a membrane separation layers, the system can use both cold weather and hot and humid weather to produce water, which it then uses to cool the air inside the data center. Facebook estimates this system can cut water usage by 20 percent.
Conclusion
There have been many innovations when it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems over the years, and the data center industry seems to be one of the industries at the forefront of this technology. Handling and taking care of the world’s information is an important job, and making sure that the information is treated properly is essential. Cooling systems are an integral part of this ecosystem, and innovations to these systems will always be meaningful.